How excessive fat tissue affects our blood vessels
New insights into vascular health in obesity
Advertisement
obesity plays a crucial role in how severely blood vessels are damaged – and this depends on where excessive fat accumulates in the body. This is the finding of a research team from the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK) and the University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG), working together with international collaborators.
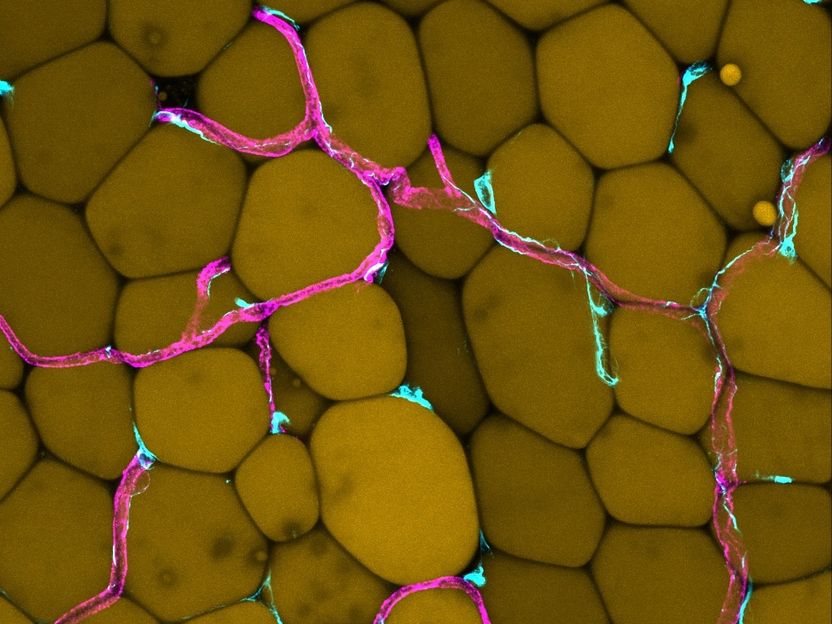
Abdominal fat in particular is considered dangerous. One reason for this is that obesity leads to a remodelling of the blood vessels, which promotes inflammation and functional disorders. The picture shows blood vessels within the white adipose tissue.
Copyright: Andreas Fischer & Sana Hasan, University Medical Centre Göttingen
Led by Prof. Andreas Fischer, director of the Department of Clinical Chemistry at the University Medical Center Göttingen, and Dr Sana Hasan, scientist at the same department, the researchers were able to show for the first time that so-called white adipose tissue in the abdomen and under the skin responds differently to overnutrition. This leads to varying degrees of damage to the blood vessels – a process that can cause inflammation, impaired blood flow, and ultimately cardiovascular disease.
Not all body fat is the same
The study adds an important piece to the puzzle of why abdominal fat is particularly harmful: in this visceral fat tissue, as it is known in medical terms, obesity triggers vascular remodeling that promotes inflammation and dysfunction. In contrast, the researchers found a special type of blood vessel cell in subcutaneous fat tissue – cells with tiny “windows” known as fenestrated endothelial cells. In a healthy state, these cells appear to support tissue function. However, in obesity, they become significantly reduced.
“Our findings show that vascular changes in obesity begin earlier than previously thought – and that they differ considerably depending on fat location,” explains Fischer. “This places the blood vessels themselves more at the center of research on obesity and metabolic diseases.”
VEGFA - a key molecule for vascular health
The team also identified an important signaling molecule necessary for maintaining vascular structure in fat tissue – VEGFA. When VEGFA levels drop, for instance due to a long-term high-fat diet, the blood vessels begin to lose both structure and function. “This mechanism can be observed not only in mice but also in human fat tissue,” says Fischer. “It opens up new strategies for preserving or restoring vascular health in obesity.”
Obesity research in unprecedented detail
The published study combines cutting-edge single-cell analyses with imaging techniques and genetic experiments, offering an unprecedented level of detail. “These results provide a valuable foundation for future therapies – such as approaches to specifically improve blood vessel function in fat tissue and prevent secondary diseases like diabetes or heart attacks,” first author of the study Hasan concludes.
Original publication
Sana S. Hasan, David John, Martina Rudnicki, Ibrahim AlZaim, Daniel Eberhard, Iris Moll, Jacqueline Taylor, Christian Klein, Maximilian von Heesen, Lena-Christin Conradi, Ralf H. Adams, Eckhard Lammert, Joanna Kalucka, Christiana Ruhrberg, Stefanie Dimmeler, Andreas Fischer; "Obesity drives depot-specific vascular remodeling in male white adipose tissue"; Nature Communications, Volume 16, 2025-6-25
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.

Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.

























































