Sartorius
Optimizing Kinetics Assays to Prevent Avidity Effects
Robust experimental design avoids artefacts in the measurement of binding kinetics and affinity
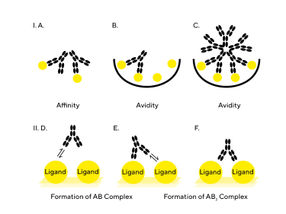
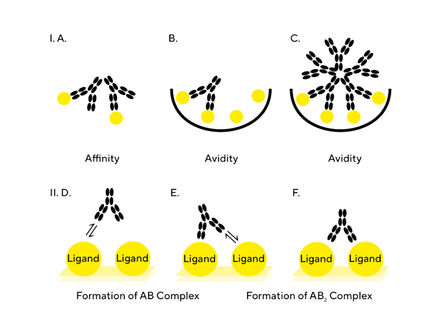
A fundamental understanding of the differences between affinity and avidity is essential when designing and developing assays for antibody development. This application note discusses the phenomena of affinity and avidity as measured with a label-free biosensor approach and how to recognize and resolve issues arising from interactions that contain a bivalent or multivalent component. Assay design plays a critical role in the ability to determine the correct binding kinetics and affinity values and therefore, key parameters including assay orientation, valency (mono- or multivalent), ligand surface density and non-specific binding (NSB) are discussed. Affinity and avidity are closely related parameters, which when considered early in assay design can ensure the user can generate the desired assay parameters between the interacting molecules.
Learn how to:Advertisement
White Paper classification
White papers on related topics
Products on related topics
Manufacturers of similar products
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous