How can life emerge in a world of minerals?
The European Research Council (ERC) has awarded an ERC Synergy Grant to the project “The role of silica at the dawn of life on our planet” (PROTOS)
Advertisement
How did our planet become habitable? The first five hundred million years of planet Earth – the so-called Hadean – have been shrouded in mystery so far because there are no remains of rocks from those times. The discovery that the planet already had water then has opened up new perspectives on a period when first forms of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms (metabolism) and self-replication could have developed. This is why a group of scientists is setting out to simulate Hadean conditions by means of laboratory experiments.
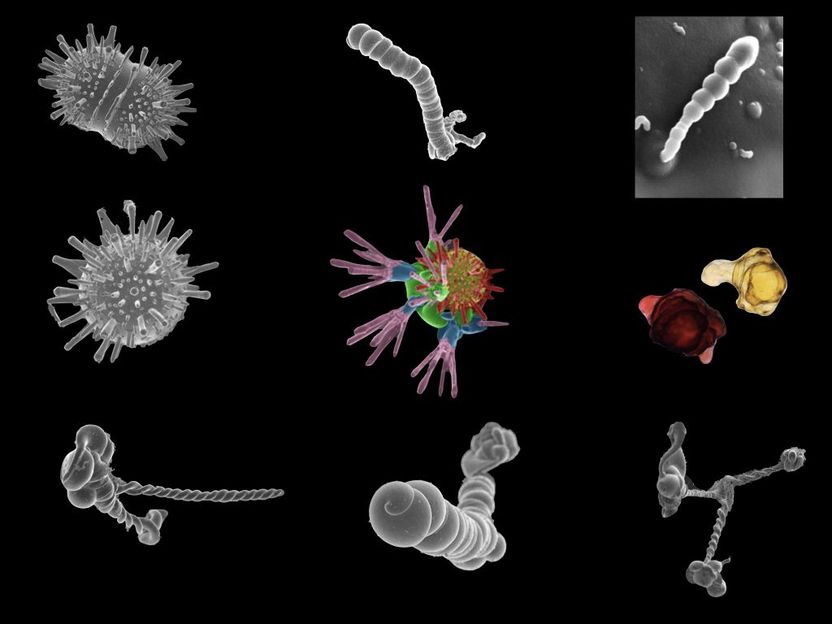
Mineral self-organizing structures called biomorphs that mimic living organisms but are the result of purely abiotic reactions. The size of these biomorphs is between one and 25 micrometers.
© Juan Manuel García-Ruiz/ CSIC
Their project “The role of silica at the dawn of life on our planet” (PROTOS) has been awarded an ERC Synergy Grant entailing funding of 9,996,000 euros over a period of 72 months, that is, until 2029. Besides project coordinator Juan Manuel Garcia Ruiz (Andalusian Earth Sciences Institute – IACT, Spanish National Research Council – CSIC), Helmut Cölfen (University of Konstanz), Wolfgang Bach (University of Bremen) and Mark van Zuilen (CNRS-Geo-Ocean, University of Brest) will participate in PROTOS.
From the mineral world to life
“We focus on the geochemical processes that took place during the first billion years of the history of this planet to investigate how life appeared from scratch, i.e., how the transition from the mineral world to life occurred. Minerals can self-organize when they come out of solution and form structures that mimic primitive forms of life”, says Juan Manuel Garcia Ruiz, project coordinator and asks: “But what is the limit of mineral self-organization, and can it seamlessly lead to life?”
For finding an answer to this question, silica is expected to have played a crucial role. “Evidence for water on earth was discovered, dating back to around 4.3 billion years ago. Water-rock reactions turned the seas alkaline and silica-rich. Silica is known to catalyze prebiotic reactions, which can produce organic molecules like amino acids, the building blocks of life”, explains Helmut Cölfen.
The physical chemist has worked on the analysis of very small species like ions, their subsequent aggregation into larger aggregates and their role in nucleation and the growth of crystals. “This analysis prepares the ground for the analysis of the silica solutions from solid-rock interaction because we expect them to be of complex composition containing multiple species like different silica oligomers. Their formation size and reactivity needs to be understood”, says Cölfen.
The Hadean simulator
PROTOS follows an experimental approach that is technically challenging. The scientists will use an array of reactors called “the Hadean simulator” to obtain information from the nanometre to the planetary scale. They will perform experiments under the earliest atmospheric conditions of Earth to reveal how fluids interact with rocks. By means of experiments, they want to find out about the role of minerals, especially silica, in triggering prebiotic reactions and mineral-organic self-organized structures leading to essential molecules for life like amino or nucleic acids. They will also research the role of silica in the fossilization and preservation of remnants of earth’s earliest microorganisms and biomorphs.
Cölfen points out: “The University of Konstanz has much of the sophisticated analytical equipment needed to perform such demanding experiments.” The synergy between the four institutions’ laboratories is expected to create a unique situation where the complex combinations of Hadean conditions can be tested in a systematic way.