Researchers lay groundwork for potential dog-allergy vaccine
Scientists have identified a series of molecular candidates for those parts of dog allergens that cause immune reactions in people
Advertisement
There have been many research efforts describing the nature and progression of dog allergies, but there have been very few applied studies that use this information to try to cure people of dog allergies entirely by artificially inducing immune tolerance. But researchers have now for the first time identified candidates for those parts of the molecules that make up dog allergens that could give us precisely that: a ”dog allergy vaccine.”

Symbolic image
pixabay.com
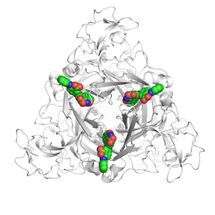
Researchers for the first time identified candidates for those parts of molecules that make up dog allergens that could give us precisely that: a "dog allergy vaccine.”
T. Inui, Osaka Prefecture University

Being allergic to dogs is a common malady and one that is growing worldwide. Over the years, scientists have been able to identify seven different dog allergens—molecules or molecular structures that bind to an antibody and produce an unusually strong immune response that would normally be harmless.
These seven are named Canis familiaris allergens 1 to 7 (Can f 1-7). But while there are seven, just one, Can f 1, is responsible for the majority (50-75 percent) of reactions in people allergic to dogs. It is found in dogs’ tongue tissue, salivary glands, and their skin.
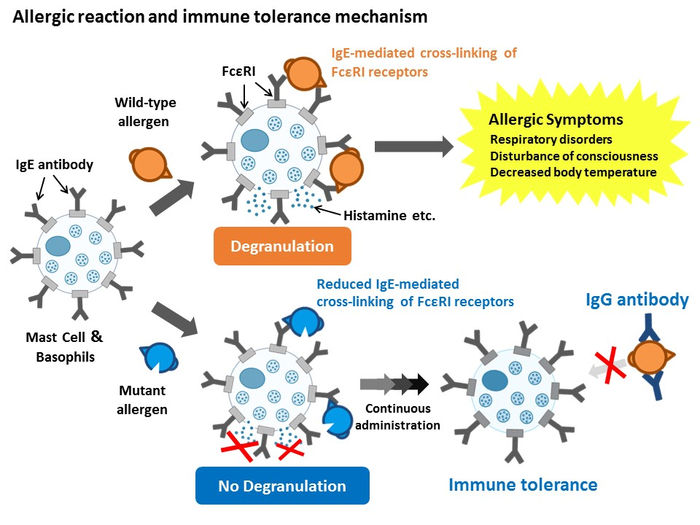
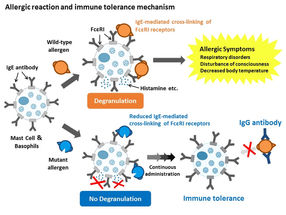
Researchers have yet to identify Can f 1’s IgE epitopes—those specific parts of the antigens that are recognized by the immune system and stimulate or ‘determine’ an immune response (which is why epitopes are also called antigen determinants). More specifically, epitopes are short amino acid sequences making up part of a protein that induces the immune response.
Epitopes bind to a specific antigen receptor on the surface of immune system antibodies, B cells, or T Cells, much like how the shape of a jigsaw puzzle piece fits the specific shape of another puzzle piece. (The part of the receptor that binds to the epitope is in turn called a paratope). Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulin, come in five different classes or isotypes: IgA (for immunoglobulin A), IgD, IgE, IgG, or IgM. The IgE isotype (only found in mammals) plays a key role in allergies and allergic diseases. There is also an IgE epitope that is the puzzle piece that fits the IgE isotype’s paratope.
In recent years, there has been extensive effort at developing epitope-focused vaccines—in this case, a vaccine against dog allergies.
“We want to be able to present small doses of these epitopes to the immune system to train it to deal with them, similar to the principle behind any vaccine,” said Takashi Inui, a specialist in allergy research, professor at Osaka Prefecture University and a lead author of the study. “But we can’t do this without first identifying the Can f 1’s IgE epitope.”
So the researchers used X-ray crystallography (in which the diffraction of x-rays through a material is analyzed to identify its ‘crystal’ structure) to determine the structure of the Can f 1 protein as a whole—the first time this had ever been done.
They found that the protein’s folding pattern is at first glance extremely similar to three other Can f allergens. However, the locations of surface electrical charges were quite different, which in turn suggest a series of ‘residues’ that are good candidates for the IgE epitope.
Using this basic data, further experimental work needs to be performed to narrow the candidates down, but the findings suggest the development of a hypoallergenic vaccine against Can f 1—a dog-allergy vaccine—is within our grasp.
The production of a ‘hypoallergenic vaccine’ by use of such epitopes would not just be a world-first with respect to dog allergies but is rare with respect to any allergic reaction. If the researchers’ work is indeed used to develop a dog allergy vaccine, the principles behind it could be used much more widely against various allergies.