Biotech Pharmacon to trial SBG/Rituxan combination therapy with Radium
Latest beta-glucan/cancer antibody study follows Herceptin
Advertisement
Biotec Pharmacon and the Norwegian Rikshospitalet - Radiumhospitalet TRUST (Department for Clinical Cancer Research) have signed a Letter of Intent to perform clinical studies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the company's pharmaceutical compound SBG in combination with cancer antibodies in patients with lymphoma.
The two parties intend to investigate if SBG in combination with cancer antibodies show higher treatment efficacy than the cancer antibodies alone. If initial studies support this concept, the parties will seek to establish broader therapeutic explorative (phase II) clinical studies, possibly with other hospitals in Norway and abroad. The parties may also agree to perform studies with other cancer types than lymphoma.
SBG from Biotec Pharmacon will first be tested in combination with the cancer antibody Rituxan (Roche) which is used in the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). It is the intention of the two parties to initiate studies during the first half of 2006.
Other news from the department research and development
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
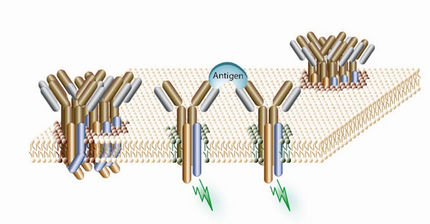
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous