Spin-off offers purification tool to tackle viral gene therapy manufacturing bottlenecks
Higher speed and increased yield thanks to membrane-based steric exclusion chromatography
Advertisement
ContiVir, a spin-off project at the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics of Complex Technical Systems Magdeburg, has published results in the scientific journal Human gene therapy detailing the purification of Adeno-associated virus (AAV) using membrane-based steric exclusion chromatography (SXC), a technology developed by Dr.-Ing. Pavel Marichal-Gallardo from the Bioprocess Engineering group headed by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Udo Reichl.
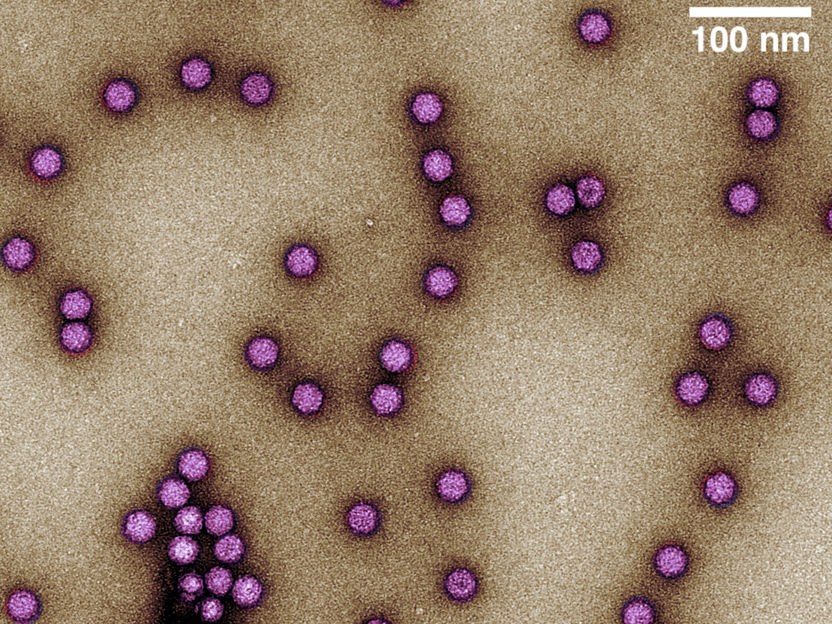
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) particles purified using ContiVir’s steric exclusion technology. The colorized image shows the icosahedral protein capsids of AAV in purple; approximate size: 25 nm.
Transmission electron microscopy, Max Planck Institute for Dynamics of Complex Technical Systems Magdeburg
Viruses can be used as vectors (vehicles) for gene delivery to treat several congenital and acquired diseases in humans. However, for efficient therapy, they are needed in very large quantities. The lack of manufacturing capacity for the huge amount of virus particles required for a single treatment is a known issue publicly expressed by several industry experts and biopharmaceutical companies.
Although the approval of the first cell and gene therapies has occurred only in recent years, the industrial manufacturing for these products still relies on technologies that are more than 30 years old and often display low product yields and even the risk of batch failures. With a growing number of gene therapies approved in the next years, a still increasing world population, and the emergence of serious public health threats such as COVID-19 that highly disrupt the biopharmaceutical supply chain, experts agree that incremental changes in production capacity with current technologies will not be enough to cope with the huge demand for virus manufacturing. New, highly efficient technologies that address these issues are urgently needed.
Higher speed, increased yield, and plug-and-play and single-use operation thanks to membrane-based steric exclusion chromatography
Dr. Julian Lopez, responsible for Business Development of the ContiVir project, commented: “Our SXC technology has many of the attributes that the gene therapy industry is after when looking at new ways to truly tackle current and future challenges in manufacturing of virus particles, such as higher speed, increased yield, and plug-and-play & single-use operation.”
Dr. Pavel Marichal-Gallardo, responsible for Downstream Processing in the ContiVir team and lead author of the scientific study published in cooperation with AAV pioneer Prof. Dr. Dirk Grimm (Heidelberg University Hospital), commented: “Our results highlight the versatility of SXC as a platform technology for several AAV variants irrespective of their surface characteristics, potentially shortening and easing process development, scale-up, and operation. In some instances, we were able to recover with the smallest SXC device an amount of AAV particles equivalent to 20 retinal gene therapy treatments in less than one hour from a cell fraction that is commonly discarded in many laboratories because they lack the capacity to process larger volumes. With SXC, this material need not go to waste. We also observed a ten times faster operation compared to other currently used purification methods.”
Prof. Grimm and Dr. Kathleen Börner, equal initial author of this study and senior scientist with Prof. Dr. med. Med. Hans-Georg Kräusslich at the University Hospital Heidelberg, add: "We are particularly pleased that this new technology is compatible with both frequently used AAV wild types and synthetic designer AAV capsid variants. These variants are constantly evolving as the result of our work and that of our colleagues. SXC is crucial for the availability of universal and scalable purification tools and their successful application in human gene therapy."
At present, the membrane-based SXC technology is being tested by several of ContiVir’s industrial collaborators that have been provided with refined single-use laboratory scale prototypes similar to the ones used for purification of AAV particles in the recently published work in Human Gene Therapy.
Julian Lopez further commented: “We have witnessed in the past months an increased interest in our SXC technology. We now have two SXC prototypes in our research portfolio that are provided for obtaining feedback from our partners for refining the product so it meets their needs and expectations. We are aiming at having several SXC models in the next months that will be suitable for production of clinical material, a key feature that has been requested by an increasing number of partners.”
The research of ContiVir is funded by the European Union and the German federal government within its EXIST Forschungstransfer program. ContiVir’s laboratory facilities are located at the Chair for Bioprocess Engineering at the Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg.
Other news from the department research and development
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Something is happening in the life science industry ...
This is what true pioneering spirit looks like: Plenty of innovative start-ups are bringing fresh ideas, lifeblood and entrepreneurial spirit to change tomorrow's world for the better. Immerse yourself in the world of these young companies and take the opportunity to get in touch with the founders.