MorphoSys Press Release: MorphoSys Successfully Concludes Therapeutic Antibody Project
MorphoSys AG announced the successful conclusion of a first therapeutic antibody program with Novartis. MorphoSys generated numerous fully human antibodies fulfilling previously defined success criteria against a cancer disease-related target molecule from Novartis, and thus achieved the first performance-related milestone in the cooperation. The amount of the associated milestone payment made to MorphoSys was not disclosed. The project work commenced in September 2004 and was completed within 11 months.
In May 2004, MorphoSys and Novartis forged a strategic antibody alliance to jointly develop new antibody-based therapeutic substances against a range of illnesses for which the current treatment is inadequate. As part of the cooperation, Novartis decided to acquire an equity stake in MorphoSys worth around EUR 9 million.
Most read news
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
From now on, don't miss a thing: Our newsletter for biotechnology, pharma and life sciences brings you up to date every Tuesday and Thursday. The latest industry news, product highlights and innovations - compact and easy to understand in your inbox. Researched by us so you don't have to.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous
Last viewed contents
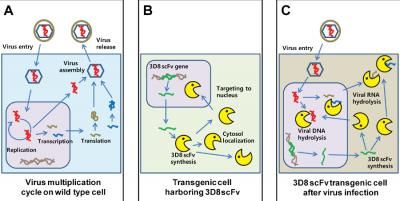
A mini-antibody with broad antiviral activity chews up viral DNA and RNA
PPD Informatics Enters Cooperative Research And Development Partnership With FDA on PPD Patient Profiles
‘Stealth’ properties of cancer-causing genetic mutations identified
Multiple_birth
Fyodor_Dostoevsky
Investment Survey Reveals Increased Confidence in Biotechnology Sector
Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. (ISC) - München, Germany