Immune system involved in rare epilepsy
Advertisement
The complement system, which forms part of our immune system, is involved in a special form of epilepsy. This is the conclusion of a recently published single-case study. The study, carried out as part of a project sponsored by the Austrian Science Fund FWF, provided useful information for patient-specific treatment.
For many years, Jan Bauer of the Centre for Brain Research at the Medical University of Vienna has been studying a specific type of epilepsy known as immune-mediated epilepsy, in which the body’s own immune system attacks brain cells and can cause damaging epileptic seizures.
Inside & outside
“Only recently it has been discovered that immune-mediated epilepsy can be divided into two groups,” Bauer explains. “In one group, the immune system attacks inner parts of brain cells. In the other, the immune system is directed against structures on the outer surface of brain cells. In principle, the latter group is more amenable to drug therapy, but we still understand too little about the actual, concrete pathogenic processes.” In an ongoing FWF project entitled “Inflammation and Viruses in Epilepsy”, Bauer is trying to identify the causes and underlying processes of this group of immune-mediated epilepsies. He recently published a description of an interesting case in collaboration with international colleagues. For the first time, the involvement of a specific part of the immune system in the progression of the disease was confirmed, enabling doctors to treat the patient.
Surgery & diagnosis
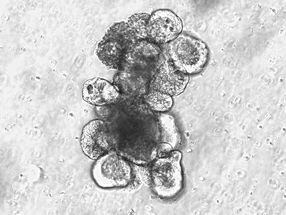
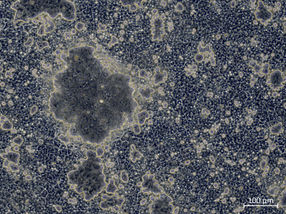
The patient who was the subject of this success was a 62-year-old who had suffered epileptic attacks and cognitive deficits for the past three years. Surgical interventions were performed, which provided Bauer’s team with tissue samples for precise analysis. The analytical results enabled the researchers to diagnose a known, but rare form of immune-mediated epilepsy known as CASPR2-antibody-associated encephalitis. In this disorder, parts of the specific immune system are directed against the CASPR2 protein, a constituent of a channel protein that regulates the potassium content of neurons and therefore affects the transmission of nerve impulses.
Antibodies & complement
In fact, thanks to Bauer’s detailed research, it was possible to identify two damaging processes in the patient’s brain. “It is highly likely that there are two processes in this condition. One process is directly due to antibodies, and the damage it causes is reversible. In the second process, the complement system of the immune system causes damage resulting in irreversible loss of brain tissue,” Bauer explains. The complement system consists of numerous proteins that are involved in fending off supposed pathogens and act partially independently of antibodies. Bauer’s team showed that the complement system plays a key role in CASPR2-associated encephalitis – a fact that was previously unknown.
Science & treatment
The scientific analyses carried out by Bauer and his team also led to specific treatment for the patient. The brain-damaging processes identified by the team were counteracted with specific medications. As a result, the patient’s steady decline was halted, and his condition even improved again to some degree.
“Although we only studied and were able to help just a single patient, thanks in part to the support of the FWF, we were able for the first time to describe a process underlying the progression of CASPR2-antibody-associated encephalitis in detail” explains Bauer, “Further studies can now be carried out for the specific purpose of confirming our observations. The findings may eventually lead to the development of effective, generally available drugs.”
Original publication
P. Körtvelyessy, J. Bauer, C. M. Stoppel, W. Brück, I. Gerth, S. Vielhaber, F. R. Wiedemann, H. J. Heinze, C Bartels, C. G. Bien; „Complement-associated neuronal loss in a patient with CASPR2 antibody–associated encephalitis“; Neurology® Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation; 2015;2:e75