How plants defend themselves
Plant immune system detects bacteria through small fatty acid molecules
Advertisement
Like humans and animals, plants defend themselves against pathogens with the help of their immune system. But how do they activate their cellular defenses? Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have now discovered that receptors in plant cells identify bacteria through simple molecular building blocks.
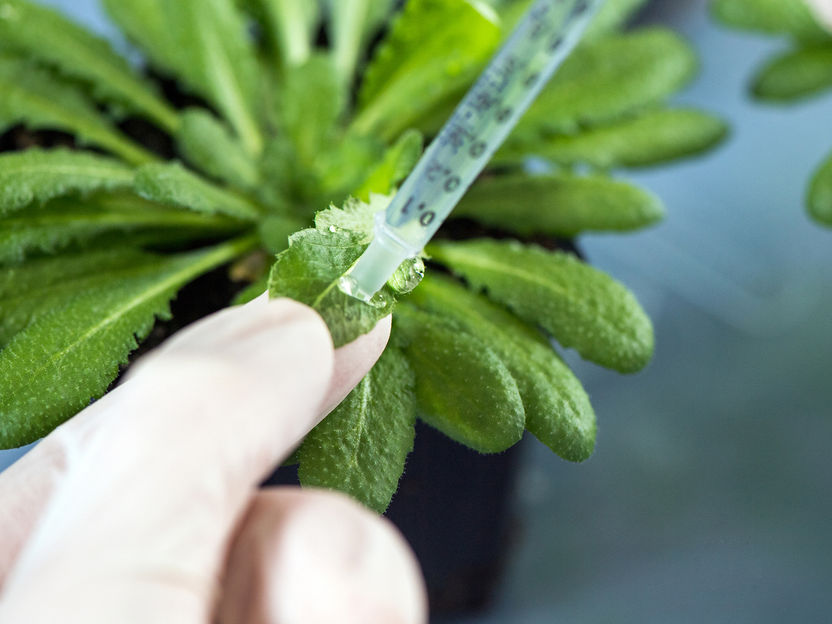

Arabidopsis thaliana leaves are infected by simply pressure-infiltrating a solution containing the bacteria.
A. Eckert / TUM
"The immune system of plants is more sophisticated than we thought," says Dr. Stefanie Ranf from the Chair of Phytopathology of the TU Munich. Together with an international research team, the biochemist has discovered substances that activate plant defense.
Until now, scientists have thought that plant cells – similar to those of humans and animals – recognize bacteria through complex molecular compounds, for example from the bacterial cell wall. In particular, certain molecules composed of a fat-like part and sugar molecules, lipopolysaccharides or LPS for short, were suspected of triggering an immune response.
In 2015, Ranf's team successfully identified the respective receptor protein: lipo-oligosaccharide-specific reduced elicitation, or LORE for short. All experiments indicated that this LORE protein activates the plant cell's immune system when it detects LPS molecules from the cell wall of certain bacteria.
A throwback leads to the right track
"The surprise came when we wanted to study this receptor protein more closely," recalls Ranf. "Our goal was to find out how LORE distinguishes different LPS molecules. For this we needed high-purity LPS. "
The researchers found that only LPS samples with certain short fatty acid constituents triggered plant defense. Surprisingly, they found in all these active LPS samples also extremely strong adhering free fatty acid molecules. Only after months of experimentation was the team able to separate these free fatty acids from the LPS.
"When we finally succeeded in producing highly purified LPS, it became apparent that the plant cell did not respond to them at all! Thus, it was clear that the immune response is not triggered by LPS, but instead by these short fatty acids" said Ranf.
Targeting bacteria building blocks
The 3-hydroxy fatty acids are very simple chemical building blocks compared to the much larger LPS. They are indispensable for bacteria and are produced in large quantities for incorporation into diverse cellular components.
"The strategy of plant cells to identify bacteria through these basic building blocks is extremely sophisticated; the bacteria require these 3-hydroxy fatty acids and therefore cannot bypass the immune response," summarizes Ranf.
Fitness program for plants
In the future, these results could help in breeding or genetically engineering plants with an improved immune response. It is also conceivable that plants treated with 3-hydroxy fatty acids would have increased resistance to pathogens.
Original publication
"Bacterial medium chain 3-hydroxy fatty acid metabolites trigger immunity in Arabidopsis plants" Alexander Kutschera, Corinna Dawid, Nicolas Gisch, Christian Schmid, Lars Raasch, Tim Gerster, Milena Schäffer, Elwira Smakowska-Luzan, Youssef Belkhadir, A. Corina Vlot, Courtney E. Chandler, Romain Schellenberger, Dominik Schwudke, Robert K. Ernst, Stéphan Dorey, Ralph Hückelhoven, Thomas Hofmann, Stefanie Ranf; Science; April 12, 2019