The dance of the chaperones
Max Planck scientists identify key player of protein folding
Advertisement
proteins are the molecular building blocks and machinery of cells and involved in practically all biological processes. To fulfil their tasks, they need to be folded into a complicated three-dimensional structure. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry (MPIB) in Martinsried near Munich, Germany, have now analysed one of the key players of this folding process: the molecular chaperone DnaK. "The understanding of these mechanisms is of great interest in the light of the many diseases in which folding goes awry, such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's," says Ulrich Hartl, MPIB director. The work of the researchers has now been published in Cell Reports.
Proteins are responsible for almost all biological functions. The cells of the human body continuously synthesize thousands of different proteins in the form of amino acid chains. In order to be biologically useful, these chains must fold into a complex three-dimensional pattern. When this difficult process goes wrong, it can lead to useless or even dangerous protein clumps. All cells, from bacteria to human, have therefore developed a network of molecular chaperones, proteins themselves, which help other proteins to fold properly.
MPIB scientists have now investigated the organisation of this network in the bacterium Escherichia coli. Using proteomic analyses they show how different chaperones cooperate during the folding process. "We identified the Hsp70 protein DnaK as the central player of the network," explains Ulrich Hartl. "It functions as a kind of turntable." DnaK binds to about 700 different protein chains as they are synthesised. Furthermore, DnaK mediates the folding of most of these protein chains. Those it cannot fold are transferred to yet another chaperone, the barrel-shaped GroEL. GroEL is a highly specialised folding machine. It forms a nano-cage in which a single protein chain is temporarily enclosed and allowed to fold while protected from external influences.
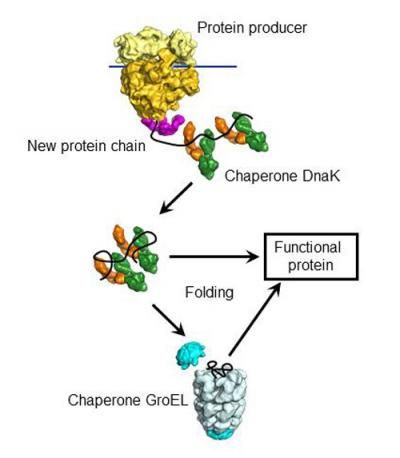
The chaperone DnaK binds to new proteins and mediates their folding. Proteins it cannot fold, DnaK transports to GroEL, a highly specialized folding machine.
MPI of Biochemistry
Disruptions in the Chaperone Network
The researchers also investigated what happens when the chaperone network is disturbed. For example, when GroEL is removed from the cells, its client proteins accumulate on DnaK, which then shuttles them to proteases to be decomposed. "Apparently, DnaK realises that the attached protein chains will never be able to mature into useful molecules," says the biochemist. Similar but even more complicated chaperone networks control the proteome of human cells. Understanding these reactions is of great interest in the light of the many neurodegenerative diseases in which folding goes awry.