New spin-out company developing wound infection tests
A quick and simple test for bacterial infections is a step closer to market
Advertisement
The University of Bath and University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHS Foundation Trust is launching a new spin-out company that is creating a quick and simple test for diagnosing bacterial infections in wounds, based on technology developed at the University’s Department of Chemistry.
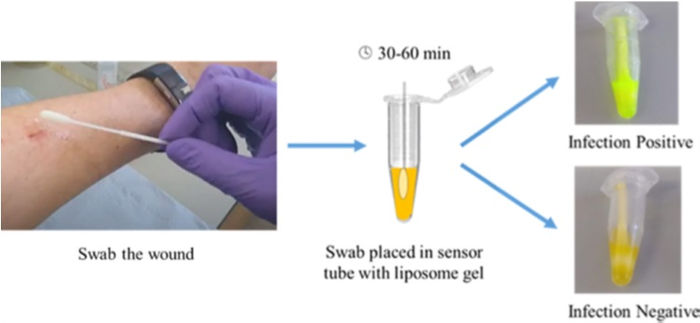
Graphic showing how the swab test works.
SmartWound Ltd
SmartWound Limited’s technology uses a colour-changing dye to diagnose bacterial infections from wound swab samples, specifically detecting when toxic bacteria are present without responding to the “good” microbes normally found on healthy skin.
A proof-of-concept study in a small group of patients performed at University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHS Foundation Trust, and Queen Victoria Hospital (East Grinstead) showed good accuracy of the technology.
The test is quick and simple to use and does not need to be sent off to a laboratory for processing, meaning clinicians can potentially spot infections earlier, allowing improved treatment for patients as well as reducing unnecessary use of antibiotics, helping combat the threat of drug-resistant bacteria.
The technology also has the potential to reduce the length of hospital stays, resulting in more streamlined and cheaper care pathways for patients.
The path to approval will be supported by the University of Graz, Diagnostic and Research Centre for Molecular BioMedicine and the Institute of Health Care Engineering with European Testing Centre of Medical Devices in Austria, which have the necessary credentials to support the market authorisation of this new diagnostic under the new EU Regulations that come into force in May 2022.
This will make commercialisation of the test possible in the European Single Market and many other developing and emerging markets that use CE-mark confirmation as reference.
Toby Jenkins, Professor of Biophysical Chemistry at the University of Bath and Scientific Advisor at SmartWound Ltd, said: “Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is seen as a major healthcare challenge by the World Health Organisation.
“Our technology will enable healthcare professionals to make better prescribing decisions, which will help reduce the spread of resistance.
“I am delighted to see this technology start the commercialisation process and to be able to collaborate with the University of Graz to make it happen.”
Alan Boyce, CEO of SmartWound said: “I am thrilled to work with these three universities. This technology will be especially valuable in developing countries where resources are limited, and an affordable and accurate diagnostic of wound infections would make a big difference.”
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Something is happening in the life science industry ...
This is what true pioneering spirit looks like: Plenty of innovative start-ups are bringing fresh ideas, lifeblood and entrepreneurial spirit to change tomorrow's world for the better. Immerse yourself in the world of these young companies and take the opportunity to get in touch with the founders.
















































