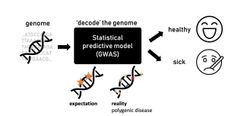
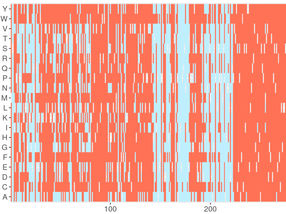
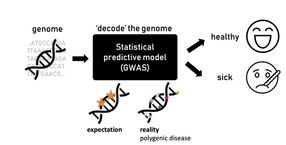
Mutations - 616 News
Tip: You can further refine your news selection by departments, organizations, countries and industries.
Mutations - 616 News
Tip: You can further refine your news selection by departments, organizations, countries and industries.
Loading...
Mutations - News by topic
Mutations - News by department
Mutations - News by industry
Mutations - News by country
Haven't found the right news yet?
The bionity.com news search
Start your targeted search now with a wide range of filter options. Our database includes an archive of 27,310 life science news from business and science, which you can search by topic and organization, filtered by time and geography.